The Appeal Board of the Japan Patent Office (JPO) decided to register a term of “bon goût” in relation to various foods of class 30 and restaurant service of class 43 by finding that the term is deemed a coined word in Japan.
[Appeal case no. 2017-7985]
“BON GOÛT”
Disputed mark (see below), written in a common font design, was filed in December 14 by designating various foods of class 30, e.g. buns and breads, confectioneries, hamburgers, pizza, hot dogs, spices, noodles, pasta, coffee, tea, and restaurant service, rental of cooking apparatus and microwave ovens and others of class 43 in the ultimate.
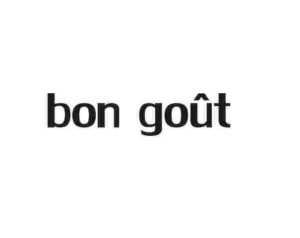
Lack of distinctiveness
JPO examiner entirely refused the mark due to lack of distinctiveness based on Article 3(1)(iii) of the Trademark Law. In refusal decision, examiner asserted the term of “bon goût” is a French term to mean “good taste” in English.
If so, relevant consumers and traders are likely to conceive the term in association with quality of goods and services.
Besides, given the mark is written in a common font design, it shall be objectionable under Article 3(1)(iii) since the mark is solely composed of elements just to indicate, in a common manner, the place of origin, place of sale, quality, raw materials, efficacy, intended purpose, quantity, shape (including shape of packages), price, the method or time of production or use.
Appeal Board decision
In the meantime, the Appeal Board overruled examiner’s rejection and granted registration of “bon goût”.
The Board admitted the terms of “bon” and “goût” are French words meaning good and taste respectively by referring to French dictionary, but, in contrast, considered a combined word of “bon goût” is unfamiliar to Japanese public with an ordinary care.
If so, disputed mark shall be deemed a coined word in its entirety and relevant consumers are unlikely to conceive any specific meaning from the mark.
Besides, the Board held, as a result of ex officio examination, there found no circumstance to convince “bon goût” is ordinarily used as a mere descriptive indication in food-service business.
Consequently, it is groundless to reject the trademark “bon goût” based on Article 3(1)(iii) since it does not give rise to any descriptive meaning in relation to the goods and services in question.
This case gives us a lesson.
Descriptive term in foreign language has a potential risk to be registered in Japan if we are unfamiliar to the term.
 Masaki MIKAMI, Attorney at IP Law – Founder of MARKS IP LAW FIRM
Masaki MIKAMI, Attorney at IP Law – Founder of MARKS IP LAW FIRM

